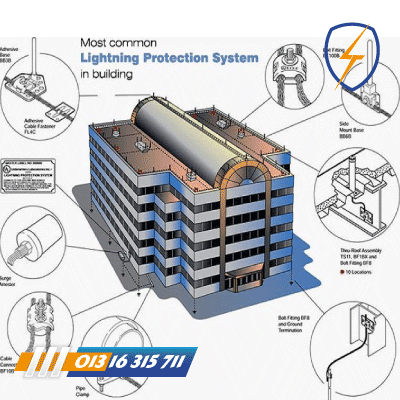
Conventional LPS
A conventional LPS (lightning protection system) refers to a traditional or standard approach to protecting a building or structure from lightning strikes. It typically consists of a set of components designed to intercept, conduct, and safely dissipate the electrical current of a lightning strike.
A lightning protection system is a set of components and equipment that are installed on a building or structure to protect it from damage caused by lightning strikes. The primary purpose of a lightning protection system is to provide a low-resistance path for the lightning current to safely pass through and into the ground, thereby reducing the likelihood of damage to the structure and its occupants.
The main components of a conventional LPS – lightning protection system include:
- Air Terminals (Lightning Rods): These are metal rods or rods with pointed tips that are strategically placed on the highest points of the structure. They provide a preferred path for the lightning to strike and help to prevent lightning from striking other vulnerable parts of the building.
- Downconductors: These are conductive cables or rods that connect the air terminals to the grounding system. They serve to conduct the lightning current from the air terminals to the ground.
- Grounding System: This is a network of conductive materials, such as copper or aluminum rods, buried in the ground. The grounding system provides a low-resistance path for the lightning current to flow into the earth, dispersing it safely.
- Bonding and Surge Protection: In addition to the main components, a conventional lightning protection system may also include bonding conductors to interconnect metal objects on the structure, such as pipes or structural components, to ensure equal potential during a lightning strike. Surge protection devices may also be installed to protect sensitive electrical and electronic equipment from voltage surges caused by lightning.
Overall, a conventional lightning protection system aims to minimize the risk of structural damage, fire, and injury by providing a path of least resistance for lightning to follow, directing it safely into the ground.



Leave a Reply